Cybersecurity Legislation: Virginia Responds to Rising Threats in the Private and Public Sectors
Employers in both the private and public sectors have had to adapt to the rise of flexible work arrangements over the past two years. However, this shift has also opened up new vulnerabilities for cyber attackers seeking to steal sensitive data. The past year saw a significant increase in cyberattacks, with hospitals, schools, and municipal governments all falling victim to crippling attacks. The Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack, which led to a gas panic in the Northeast U.S., was just one example of the damage that can be done.
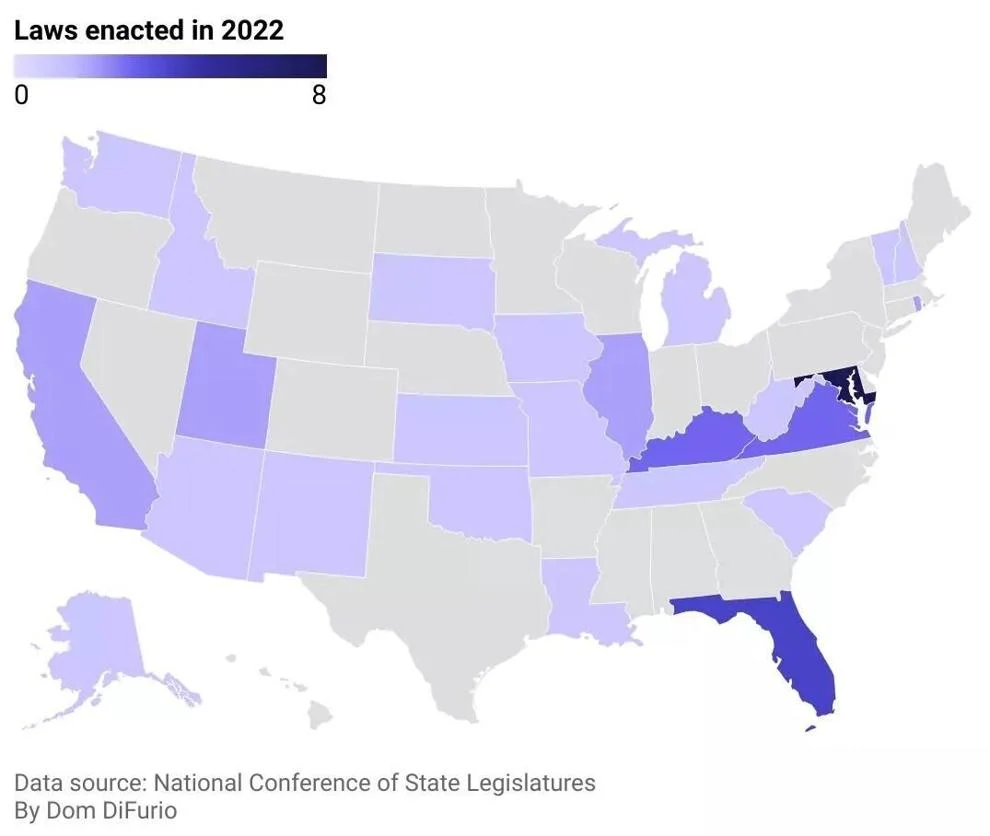
Governments have taken notice of the growing threat of cybercrime, with lawmakers passing dozens of new laws in 2022 aimed at improving cybersecurity. Drata, a cybersecurity company, compiled a list of new legislation in Virginia related to cybersecurity through February 2023. The data, collected by the National Conference of State Legislatures, reveals that Maryland passed the most cybersecurity-related laws in the past year, with eight enacted. Florida came in second with four laws, while Virginia and Kentucky tied for third with three each.
The State of Cybersecurity in 2021
Significant Cyberattacks in 2021
2021 was a year marked by an alarming increase in cyberattacks that impacted both public and private sectors. Several high-profile attacks made headlines, including the SolarWinds breach, which affected multiple government agencies and private companies, and the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack that caused gas shortages and price increases.
Other notable attacks included the Accellion data breach, which exposed sensitive information of multiple organizations, and the Microsoft Exchange Server hack, which affected thousands of organizations worldwide. These attacks showcased the increasing sophistication and persistence of cybercriminals and underscored the need for stronger cybersecurity measures.
Impact on Private and Public Sectors
The impact of cyberattacks in 2021 was significant, with businesses and government agencies alike struggling to respond to the threats. The Colonial Pipeline attack, for example, disrupted fuel supply chains and caused panic among consumers. The SolarWinds breach, on the other hand, compromised sensitive government and corporate data, raising concerns about national security.
The attacks also highlighted the importance of cybersecurity for businesses and organizations of all sizes. Small and medium-sized businesses were particularly vulnerable, with many lacking the resources and expertise to adequately protect themselves from cyber threats.
In response, lawmakers across the country passed new cybersecurity legislation aimed at improving cybersecurity education, training workers, and securing government agencies. Maryland, Florida, Virginia, and Kentucky were among the states that passed the most cybersecurity-related laws in 2022.
Overall, the state of cybersecurity in 2021 was marked by a growing awareness of the threat posed by cybercriminals and a recognition of the need for stronger cybersecurity measures. As businesses and government agencies continue to adapt to the changing threat landscape, it is clear that cybersecurity will remain a critical priority in the years to come.
Response from Lawmakers
Overview of Cybersecurity Legislation in 2022
In response to the increased threat of cyberattacks, lawmakers across the United States have been passing legislation aimed at improving cybersecurity measures. In 2022, dozens of laws were passed, with a particular emphasis on training workers, securing government agencies, and funding cybersecurity education programs.
The National Conference of State Legislatures has been tracking the passage of cybersecurity-related legislation, and the data shows that Maryland was the state with the most laws enacted, with eight in total. Florida followed with four, and Virginia and Kentucky tied for third with three laws each.
Top States Passing Cybersecurity Legislation
Maryland’s eight laws covered a range of cybersecurity issues, including data breach notification requirements, cybersecurity standards for government contractors, and the creation of a cybersecurity council.
Florida’s laws focused on cybersecurity education and training, with a particular emphasis on protecting schools and students. One law required school districts to implement cybersecurity awareness training for all employees, while another established a grant program to fund cybersecurity training programs for K-12 students.
In Virginia, the three laws passed included measures to improve cybersecurity for state agencies and critical infrastructure, as well as a requirement for state contractors to meet certain cybersecurity standards.
Kentucky’s laws addressed similar issues, with a focus on improving cybersecurity for state agencies and creating a cybersecurity awareness program for state employees.
Overall, the passage of these laws demonstrates a growing recognition of the importance of cybersecurity in both the public and private sectors. As the threat of cyberattacks continues to evolve, it is likely that lawmakers will continue to take steps to improve cybersecurity measures and protect sensitive data.
The Role of Employers in Cybersecurity
As the world grapples with the increasing threat of cyberattacks, employers in both the private and public sectors have a crucial role to play in protecting their organizations from attackers looking to steal and sell data. With the advent of flexible work over the last two years, employers are facing new challenges when it comes to cybersecurity.
Challenges of Flexible Work
The rise of remote work and flexible work arrangements has created new challenges for employers in terms of cybersecurity. With employees accessing sensitive data from a variety of devices and locations, it can be difficult to ensure that data is secure. Employers must ensure that all devices used by employees to access company data are secure, and that employees are trained on best practices for keeping data safe.
Additionally, employers must ensure that their networks and systems are secure, even when employees are working remotely. This means implementing strong security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption, as well as monitoring network activity for signs of suspicious behavior.
Protecting Organizations from Attackers
In addition to the challenges posed by flexible work, employers must also protect their organizations from cyberattacks. Cybercriminals are becoming increasingly sophisticated, using tactics such as social engineering and ransomware to gain access to sensitive data.
Employers can take a number of steps to protect their organizations from these threats. These include:
- Conducting regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities in their systems and networks
- Implementing strong authentication protocols to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data
- Providing regular cybersecurity training to employees to ensure that they are aware of the latest threats and best practices for keeping data safe
- Implementing a data backup and recovery plan in case of a cyberattack or other disaster
By taking these steps, employers can help protect their organizations from cyberattacks and ensure that sensitive data remains secure.





